UDN
Search public documentation:
SoundCueReference
日本語訳
中国翻译
한국어
Interested in the Unreal Engine?
Visit the Unreal Technology site.
Looking for jobs and company info?
Check out the Epic games site.
Questions about support via UDN?
Contact the UDN Staff
中国翻译
한국어
Interested in the Unreal Engine?
Visit the Unreal Technology site.
Looking for jobs and company info?
Check out the Epic games site.
Questions about support via UDN?
Contact the UDN Staff
Sound Cue Reference
Overview
Attenuation Node
 Attenuation
Attenuation
- Attenuate - If true, the node will fade the input sound out over distance.
- Spatialize - If true, the node will position the input sound in 3D space.
- dB Attenuation At Max - Sets the volume at the max distance in deciBels.
- Distance Algorithm - Sets the interpolation method to use when attenuating the input sound.
- ATTENUATION_Linear - Attenutes the input sound linearly over distance.
- ATTENUATION_Logarithmic - Attenuates the input sound logarithmically over distance.
- ATTENUATION_Inverse - Attenuates the input sound using an inverse function over distance.
- ATTENUATION_LogReverse - Attenuates the input sound using a reverse logarithmic function over distance.
- ATTENUATION_NaturalSound - Attenuates the input sound using a special function that approximates the way sound naturally attenuates over distance.
- Distance Type - Sets the special attenuation mode to use.
- SOUNDDISTANCE_Normal - Normal attenuation over distance in all axes.
- SOUNDDISTANCE_InfiniteXYPlane - Only attenuate the input sound using the distance in the Z-axis.
- SOUNDDISTANCE_InfiniteXZPlane - Only attenuate the input sound using the distance in the Y-axis.
- SOUNDDISTANCE_InfiniteYZPlane - Only attenuate the input sound using the distance in the X-axis.
- Radius Min - Distance from the sound's origin where attenuation should begin to occur. The input sound plays at 100% volume between 0.0 and this distance.
- Radius Max - Distance from the sound's origin where attenuation should be completed. The input sound fades from 100% to 0% between Radius Min and this distance.
- Attenuate With LPF - If true, attenuation via low pass filter is enabled.
- LPFRadius Min - Sets the distance from the sound's origin where the low pass filter should begin to be applied.
- LPFRadius Max - Sets the distance from the sound's origin where the maximum amount of low pass filter should be applied.
Concatenator Node
 Sound Node Concatenator
Sound Node Concatenator
- Input Volume - List of volumes to use for each of the input sounds allowing normalization for sounds with different source volumes.
Delay Node
 Delay
Delay
- Delay [Min/Max] - Sets the [minimum/maximum] amount of time the Delay Node should pause for.
Distance CrossFade Node
 Sound Node Distance CrossFade
Sound Node Distance CrossFade
- Cross Fade Input - List of input sounds to cross fade. Each has the following properties:
- Fade In Distance [Start/End] - Sets the distance from the sound cue's origin to [begin/complete] fading in to this input sound.
- Fade Out Distance [Start/End] - Sets the distance from the sound cue's origin to [begin/complete] fading out from this input sound.
- Volume - Sets the volume of this sound when completely faded in.
Looping Node
 Looping
Looping
- Loop Indefinitely - If true, the input sound will loop indefinitel regardless of the values of Loop Count Min and Loop Count Max.
- Loop Count [Min/Max] - Sets the [minimum/maximum] number of times the input sound should loop.
Mixer Node
 Sound Node Mixer
Sound Node Mixer
- Input Volume - List of volumes to use for each of the input sounds allowing normalization for sounds with different source volumes.
Modulator Node
 Modulation
Modulation
- Pitch [Min/Max] - Sets the [minimum/maximum] pitch for the input sound.
- Volume [Min/Max] - Sets the [minimum/maximum] volume for the input sound.
Continuous Modulator Node
 Sound Node Modulator Continuous
Sound Node Modulator Continuous
- [Pitch/Volume] Modulation - Distribution for controlling the [pitch/volume] of the input sound. Defaults to a Uniform distribution, but can be changed in the editor to any other type.
Oscillator Node
 Oscillator
Oscillator
- Modulate [Volume/Pitch] - If true, [volume/pitch] modulation is enabled.
- Amplitude [Min/Max] - Amplitude of the sine wave's modulation, centered around the value 1. For example, an Amplitude of .25 would modulate between the values .75 and 1.25 [Min/Max] fields are provided for randomization.
- Frequency [Min/Max] - Frequency of the sine wave's modulation, with the value divided by two to equal to the hertz rate. For example, a Frequency of 20 would oscillate at 10 hz (times per second). [Min/Max] fields are provided for randomization.
- Offset [Min/Max] - Offset value into the sine wave; commonly called phase. Any value here will be multiplied by 2*Pi. [Min/Max] fields are provided for randomization.
- Center [Min/Max] - A center of .5 would oscillate around .5 [Min/Max] fields are provided for randomization.
Random Node
 Sound Node Random
Sound Node Random
- Weights - List of weights for each input sound determining the odds that a particular sound will be chosen.
- Randomize Without Replacement - If true, once a sound is chosen it will not be able to be played again until all input sounds have been played.
Examples
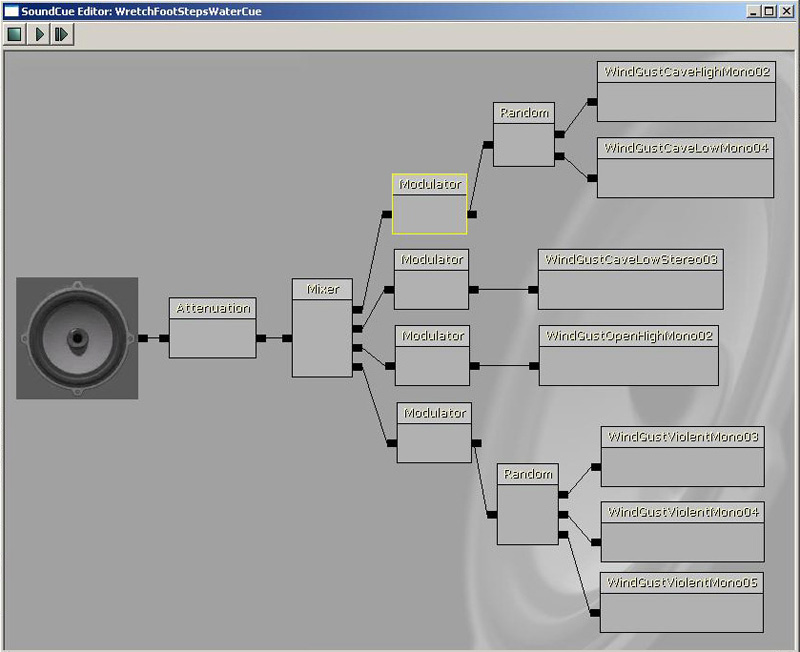 This plays four audio files simultaneously upon trigger with random variation upon retrigger.
This plays four audio files simultaneously upon trigger with random variation upon retrigger.
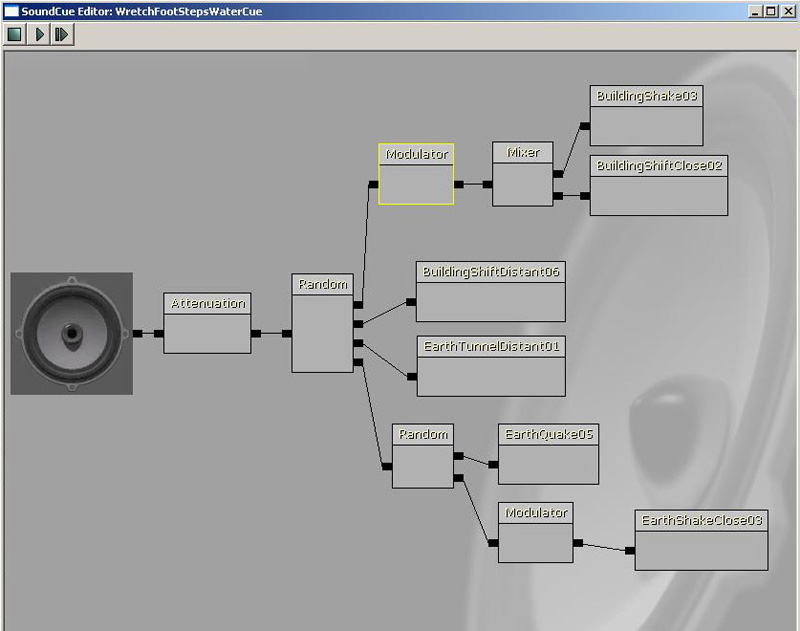 This plays one audio file upon trigger with random variations upon retrigger.
This plays one audio file upon trigger with random variations upon retrigger.
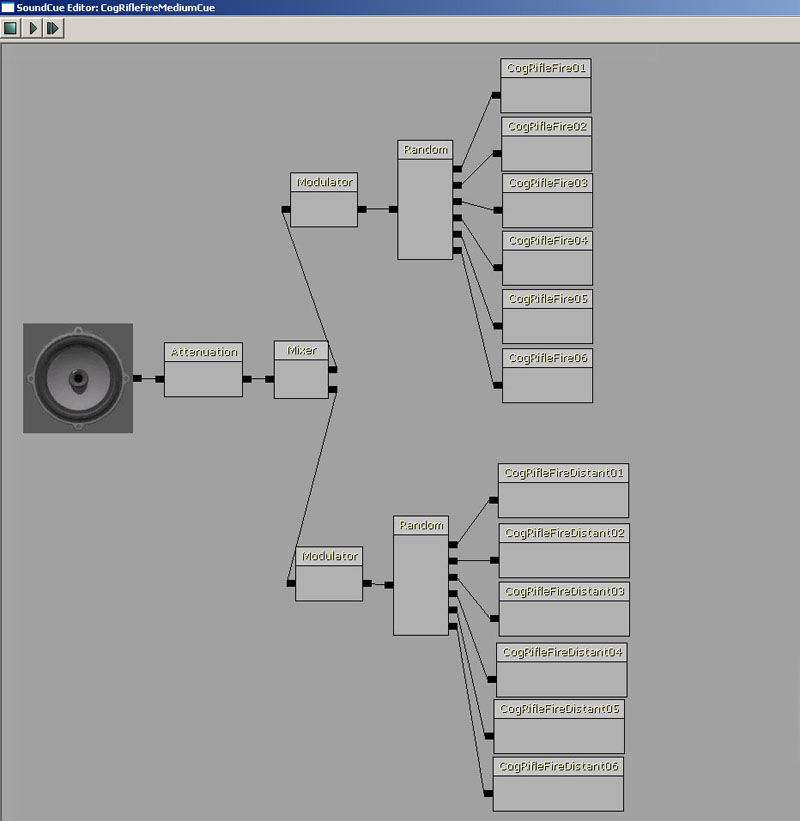 This mixes two sets of randomly triggered audio files
This mixes two sets of randomly triggered audio files
